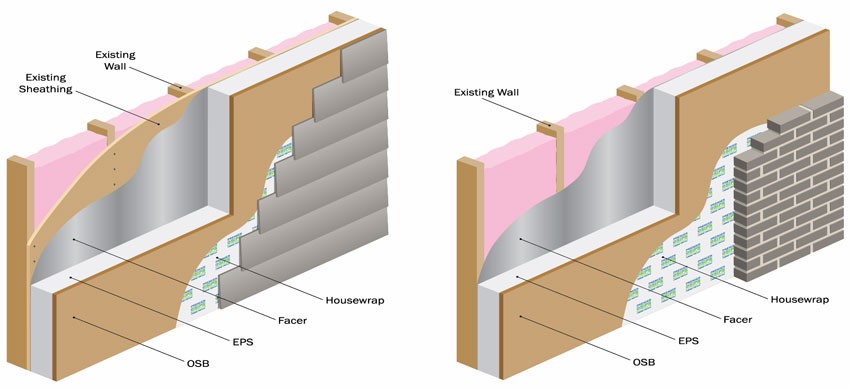
Long Lasting Insulated Siding: A Comprehensive Guide delves into the world of durable and energy-efficient exterior cladding. This guide explores the various types of insulated siding available, their installation processes, cost considerations, and long-term benefits. We’ll cover everything from choosing the right siding for your climate and home style to troubleshooting common issues and ensuring a successful installation that enhances both your home’s aesthetic appeal and its energy efficiency.
We aim to provide you with a complete understanding of insulated siding, empowering you to make informed decisions that improve your home’s value, comfort, and environmental footprint. From material selection and installation techniques to maintenance and cost analysis, this guide serves as your comprehensive resource for all things related to long-lasting insulated siding.
Introduction to Long-Lasting Insulated Siding
Long-lasting insulated siding represents a significant advancement in exterior home cladding. It combines the protective qualities of traditional siding with an integrated insulation layer, offering superior energy efficiency and durability compared to traditional materials. This comprehensive guide will explore the benefits, features, and considerations involved in choosing and maintaining this increasingly popular siding option.
Insulated siding provides numerous advantages over alternatives such as vinyl, wood, or fiber cement. Its integrated insulation reduces energy loss through the walls, leading to lower heating and cooling bills. Furthermore, it often requires less maintenance due to its inherent durability and resistance to the elements. Compared to wood, it requires less painting and is less susceptible to insect damage; compared to vinyl, it offers superior insulation and impact resistance; and compared to fiber cement, it is often lighter and easier to install.
Key Features Contributing to Longevity
Three primary features contribute to the exceptional lifespan of insulated siding. First, the integrated insulation acts as a thermal barrier, protecting the siding material from extreme temperature fluctuations that can cause expansion, contraction, and cracking. Second, the outer cladding layer, often made of durable materials like vinyl, fiber cement, or engineered wood, is designed to withstand harsh weather conditions, including strong winds, heavy rain, and intense sunlight. Third, the manufacturing process of many insulated siding systems involves advanced bonding techniques, ensuring a strong, cohesive structure that resists damage and degradation over time. These factors combine to provide a product with a significantly longer lifespan than many traditional siding options.
Guide Structure Overview
This guide is structured to provide a comprehensive understanding of long-lasting insulated siding. We will begin with an introduction to the material and its benefits, followed by a detailed exploration of different types of insulated siding available on the market. Next, we will examine the installation process, including considerations for proper preparation and techniques for achieving optimal results. Finally, we will cover maintenance and repair strategies to help you maximize the lifespan of your insulated siding investment. This guide aims to equip you with the knowledge necessary to make an informed decision and enjoy the long-term benefits of this superior siding option.
Types of Long-Lasting Insulated Siding
Choosing the right insulated siding is a crucial decision impacting your home’s curb appeal, energy efficiency, and long-term maintenance. This section will explore three common types, comparing their durability, cost, and aesthetic features to help you make an informed choice. We will also delve into the maintenance requirements for each, enabling you to budget effectively for upkeep.
Insulated Vinyl Siding
Insulated vinyl siding is a popular choice due to its affordability and low maintenance. It consists of a vinyl outer layer bonded to an insulating foam core, typically made of polyurethane or polyisocyanurate. The vinyl exterior offers a wide variety of colors and styles, mimicking the look of wood, brick, or stone. Its durability is generally good, resisting rot, insect damage, and moisture. However, it can be susceptible to damage from severe impacts, and extreme temperature fluctuations may cause slight expansion and contraction. Maintenance is minimal, usually requiring only occasional cleaning with soap and water. Replacing damaged panels is relatively straightforward and inexpensive.
Insulated Fiber Cement Siding
Fiber cement siding, a composite material made of cement, cellulose fibers, and other additives, offers superior durability compared to vinyl. It’s highly resistant to fire, rot, insects, and impact damage. Aesthetically, it provides a more natural look, often mimicking wood grain textures quite convincingly. While more expensive than vinyl, its longevity and low maintenance requirements can offset the initial higher cost over the siding’s lifespan. Regular cleaning with a pressure washer and occasional repainting (every 10-15 years depending on climate) are the primary maintenance tasks.
Insulated Foam Siding
Insulated foam siding, often made of polyurethane or polyisocyanurate, boasts exceptional insulating properties, leading to significant energy savings. Its lightweight nature makes installation relatively easy. However, it’s less durable than vinyl or fiber cement, being more susceptible to damage from impacts and UV exposure. The aesthetic options are generally more limited than vinyl or fiber cement, although textured finishes are available. Maintenance involves occasional cleaning and potentially replacing damaged sections, which can be more challenging than with other siding types due to the foam’s composition.
Comparison of Insulated Siding Types
The following table summarizes the key differences between these three types of insulated siding:
| Material | Durability | Cost | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insulated Vinyl | Good; susceptible to impact damage | Low to Moderate | Low; occasional cleaning |
| Insulated Fiber Cement | Excellent; highly resistant to damage | Moderate to High | Moderate; periodic cleaning and repainting |
| Insulated Foam | Fair; susceptible to impact and UV damage | Moderate | Moderate; occasional cleaning and potential section replacement |
Final Wrap-Up
Investing in long-lasting insulated siding is a significant decision that impacts both your home’s appearance and its energy performance. By carefully considering the factors discussed in this guide—from material selection and installation to maintenance and cost analysis—you can ensure a successful project that provides years of reliable protection and enhanced energy efficiency. Remember to choose a reputable installer and prioritize regular maintenance to maximize the lifespan and benefits of your investment. This comprehensive guide equips you with the knowledge to make an informed choice, leading to a beautiful and energy-efficient home for years to come.