Wood Insulated Siding: A Comprehensive Guide delves into the world of energy-efficient and aesthetically pleasing exterior cladding. This guide explores the various types of wood used, their manufacturing processes, and the unique advantages they offer homeowners. We’ll examine the installation process, maintenance requirements, and long-term cost considerations, comparing wood insulated siding to other popular options. Prepare to discover the enduring beauty and practical benefits of this versatile building material.
From understanding the composition of wood insulated siding and its historical evolution to mastering the installation techniques and addressing common maintenance issues, this guide provides a holistic understanding. We’ll also analyze the environmental impact and cost-effectiveness of this choice, empowering you to make an informed decision for your home improvement projects.
Introduction to Wood Insulated Siding
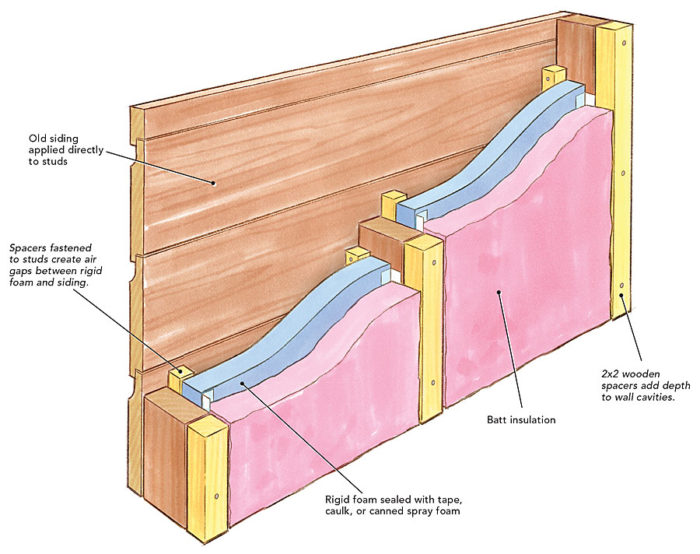
Wood insulated siding represents a modern approach to exterior cladding, combining the aesthetic appeal of wood with the energy efficiency of insulation. This innovative material offers a compelling alternative to traditional wood siding, addressing both aesthetic and practical concerns for homeowners and builders. Its unique composition and manufacturing process contribute to its superior performance characteristics.
Wood insulated siding is a composite material, typically consisting of a wood exterior layer, a core of insulating foam, and sometimes a backing layer for added stability and moisture resistance. The exterior wood layer provides the visual appeal and natural texture associated with traditional wood siding. This layer can be made from various wood species, each offering unique grain patterns, colors, and durability characteristics. The insulating foam core, often made of polyurethane or polyisocyanurate, significantly improves the thermal performance of the siding, reducing energy loss and lowering heating and cooling costs. A backing layer, when present, often consists of a moisture-resistant material like a treated wood fiberboard or a composite material, providing additional protection against moisture intrusion and enhancing the overall structural integrity of the panel.
Composition of Wood Insulated Siding
The precise composition of wood insulated siding varies depending on the manufacturer and specific product line. However, the fundamental components remain consistent. The outer layer, usually made from a durable wood species like cedar, redwood, or pine, is meticulously treated to resist rot, decay, and insect infestation. This treatment often involves pressure-treating the wood with preservatives, ensuring longevity and reducing maintenance requirements. The insulating core, generally polyurethane or polyisocyanurate foam, is strategically positioned between the outer wood layer and the backing layer (if present). This foam provides excellent thermal resistance, significantly improving the building’s energy efficiency. The backing layer, if included, acts as a moisture barrier, preventing water damage and improving the overall performance and lifespan of the siding. Variations in thickness and composition of each layer affect the final product’s R-value (thermal resistance) and overall cost.
Manufacturing Process of Wood Insulated Siding
The manufacturing process of wood insulated siding involves several precise steps. First, the chosen wood species is carefully milled and treated to ensure durability and resistance to the elements. Then, the insulating foam core is manufactured separately, often using a continuous process to ensure consistent thickness and density. The wood layer and the foam core are then bonded together using a high-strength adhesive, often under controlled temperature and pressure conditions to ensure a strong and durable bond. If a backing layer is used, it’s added to the foam core before or after the wood layer is applied. Finally, the completed panels are cut to the desired length and inspected for quality control before packaging and distribution. The entire process is designed to minimize waste and ensure consistent quality.
History and Evolution of Wood Insulated Siding
While the use of wood for exterior cladding dates back centuries, the concept of wood insulated siding is a relatively recent development. The evolution has been driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient building materials and the desire for low-maintenance exterior finishes. Early attempts at combining wood and insulation often involved separate installation processes, leading to higher costs and potential gaps in the insulation layer. However, advancements in adhesive technology and manufacturing processes have led to the development of integrated wood insulated siding panels, where the wood and insulation are bonded together during manufacturing, creating a seamless and efficient system. This innovation has made wood insulated siding a more viable and attractive option for both residential and commercial construction projects. The ongoing trend is towards even more sustainable materials and improved manufacturing techniques, further enhancing the performance and environmental friendliness of this product.
Advantages of Wood Insulated Siding
Wood insulated siding offers a compelling combination of aesthetic appeal, energy efficiency, and durability, making it a superior choice for many homeowners. Its unique construction, combining the beauty of wood with the insulating properties of a foam core, provides significant advantages over traditional siding materials. This section will delve into the key benefits of choosing wood insulated siding for your home.
Energy Efficiency Benefits
Wood insulated siding significantly improves a home’s energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer. The foam core acts as a thermal barrier, preventing heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. This results in lower energy bills and a more comfortable living environment. For example, studies have shown that homes with wood insulated siding can experience a reduction in heating and cooling costs of up to 30%, depending on factors such as climate and existing insulation levels. This translates to substantial long-term savings and a reduced carbon footprint. The R-value of the insulation core is a key factor determining the level of energy savings; higher R-values indicate better insulation performance. The exact R-value will vary depending on the thickness and type of foam core used in the siding.
Aesthetic Appeal and Curb Appeal Enhancement
Wood insulated siding offers a classic and timeless aesthetic appeal that enhances the curb appeal of any home. The natural beauty of wood provides a warm and inviting look, unlike the sometimes sterile appearance of vinyl or other synthetic materials. Homeowners can choose from a variety of wood species, stains, and finishes to perfectly complement their home’s architectural style and personal preferences. The clean lines and consistent texture of the siding create a polished and sophisticated appearance, increasing the overall value and attractiveness of the property. Imagine a charming Victorian home with richly stained cedar siding, or a modern farmhouse accented with rustic-looking reclaimed wood – the possibilities are endless.
Durability and Longevity
Wood insulated siding, when properly installed and maintained, boasts exceptional durability and longevity. The foam core protects the wood from moisture damage, rot, and insect infestation, extending its lifespan significantly compared to traditional wood siding. While all wood siding requires some level of maintenance, the protected nature of insulated siding reduces the frequency and intensity of necessary upkeep. Unlike vinyl siding, which can crack, fade, or become brittle over time, wood insulated siding retains its beauty and structural integrity for many years, providing a long-term, cost-effective solution for exterior cladding. With proper care, including regular cleaning and occasional repainting or restaining, wood insulated siding can easily last for 50 years or more.
Conclusion
Choosing the right siding for your home is a significant decision impacting both aesthetics and long-term value. This comprehensive guide has explored the multifaceted world of wood insulated siding, highlighting its strengths and weaknesses. By weighing the advantages of energy efficiency, durability, and curb appeal against the considerations of maintenance and cost, you can confidently assess if wood insulated siding aligns with your needs and budget. Remember to consult with professionals for personalized advice and installation.